HemeLB
Software for high performance parallel lattice-Boltzmann simulations for large scale fluid flow in vascular geometries
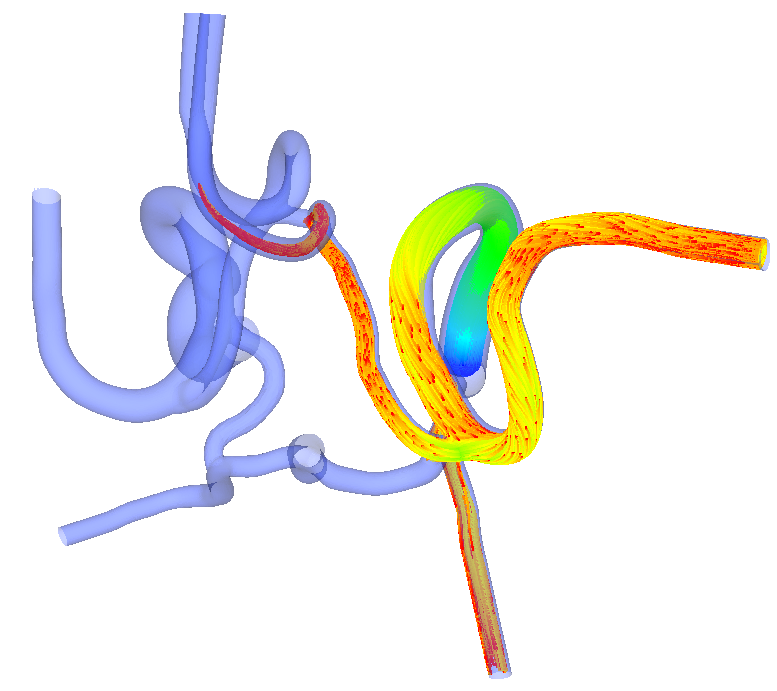
Software for high performance parallel lattice-Boltzmann simulations for large scale fluid flow in vascular geometries

HemeLB is a high performance lattice-Boltzmann solver optimized for simulating blood flow through sparse geometries, such as those found in the human vasculature. It is routinely deployed on powerful supercomputers, scaling to hundreds of thousands of cores even for complex geometries . HemeLB has traditionally been used to model cerebral bloodflow and vascular remodelling in retinas , but is now being applied to simulating the fully coupled human arterial and venous trees.
This work forms part of the fast growing field of Computational Biomedicine. Physiology and medicine are being revolutionised by the growing role of information technology. Our ability to acquire and manage data on both animals and humans allows us to develop increasingly detailed computational models of the biological processes sustaining life. These models, together with the relevant experimental data, are helping researchers to gain insight into the physiology and pathology of the systems under study, in many cases beyond what is possible with purely observational methods.